Try it:

Below you’ll see some example python code writes to a file called instructions.txt
Press Ctrl + Enter to run the code.
This code will read a list of jobs from the file todo.csv and then display which jobs are marked as being done and which ones are marked as being not completed yet:
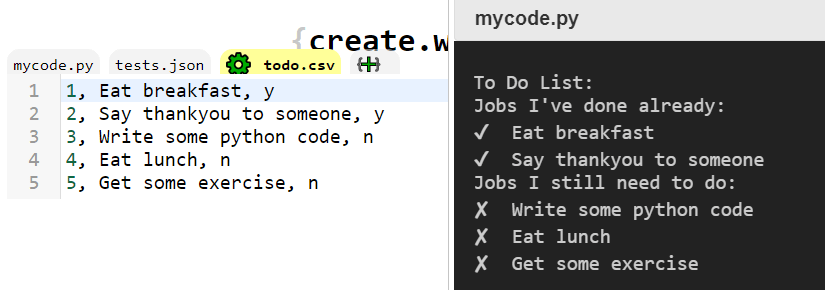
Challenges:
Start by running the code.
- Add another job to
todo.csv
The format for the CSV file is
number,task,done (y/n)– add a new line to the filetodo.csvdescribing a task (e.g. brush your teeth) - Make a variable called
remaining_jobswhich stores the number of jobs which haven’t been done yet
There are two main ways you can do this. You could set
remaining_jobsto zero at the start of the program and increase it by one every time you add a task to the listjobs_to_door you could use thelen()function to count how many items are in thejobs_to_dolist - Make a variable called
total_jobswhich stores the total number of jobs (done or not done yet)
You could count how many lines are in the CSV file or you could add up the number of items in both
jobs_to_doandjobs_done
On the next page you’ll get some code with both syntax and logic errors
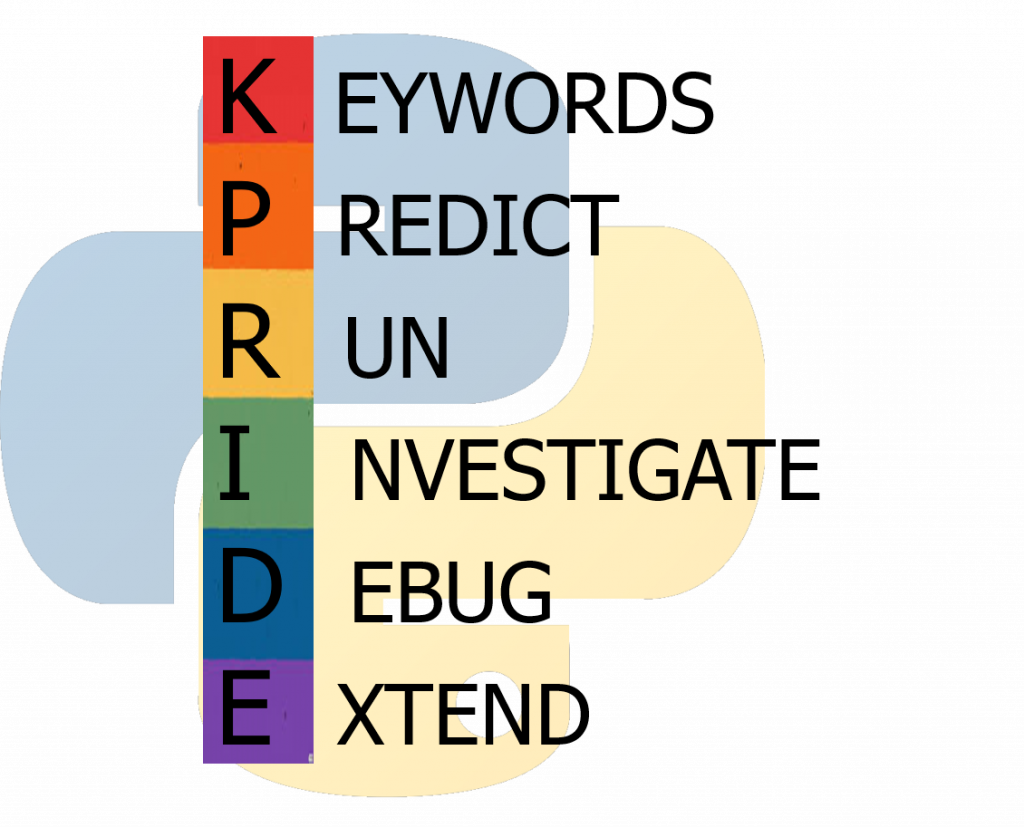
KPRIDE
KPRIDE stands for Keywords, Predict, Run, Investigate, Debug and Extend and it’s a way of helping you explore and understand python code. Click on the image below for a set of KPRIDE activities for this python skill.
Page 1: Intro
Page 2: The theory: learn what you need to know as fast as possible.
Page 3: Try it: try out and adapt some working python code snippets.
Page 4: Debug it: Learn how to find and fix common mistakes.
Page 5: Extend it: Choose a project idea to use your newfound python skills.